The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI), Government of India, has unveiled the 26th edition of its flagship publication, “Women and Men in India 2024: Selected Indicators and Data.” This annual report offers a detailed snapshot of gender-based trends and developments across multiple domains such as education, health, economic participation, and decision-making.
Sourced from various ministries, departments, and organizations, the publication presents gender-disaggregated data that highlights both progress and persistent gaps. It serves as an essential tool for policymakers, researchers, and stakeholders seeking to promote gender-sensitive and inclusive development policies.
Key Highlights from the Report
Education:
The Gender Parity Index (GPI) remains strong at both the primary and higher secondary education levels, suggesting sustained female enrolment. While upper primary and elementary levels showed some fluctuations, they remained close to achieving parity.
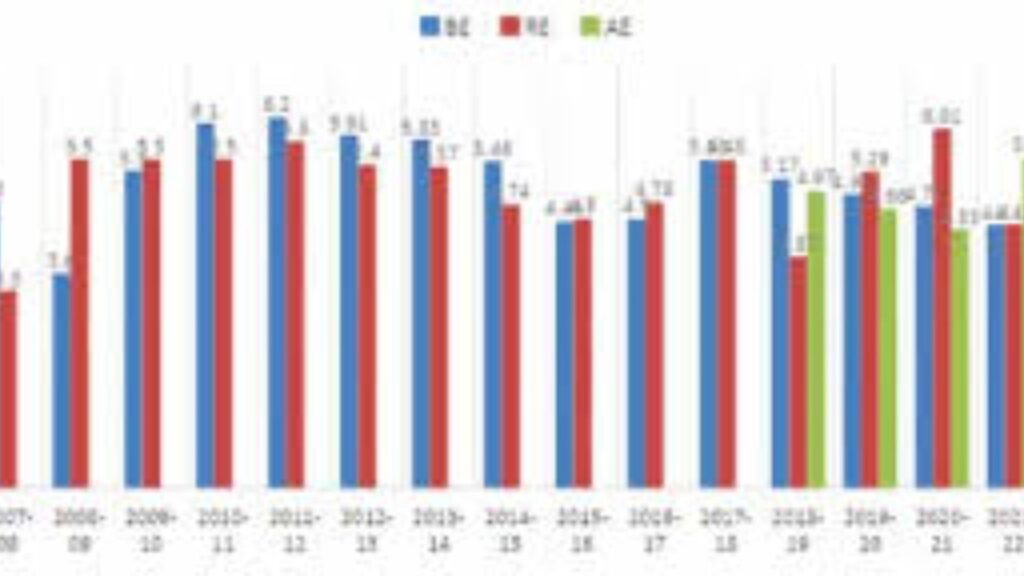
Labour Participation:
India has seen a significant rise in Labour Force Participation Rate (LPFR) for individuals aged 15 years and above. The LPFR increased from 49.8% in 2017–18 to 60.1% in 2023–24, indicating improved engagement of the population in economic activities.
Financial Inclusion:
Women now hold 39.2% of total bank accounts and contribute 39.7% of all deposits. Notably, rural areas show a higher level of female participation, with 42.2% of account holders being women.
Stock Market Participation:
There has been a remarkable rise in DEMAT accounts, reflecting increased public interest in equity markets. The number of DEMAT accounts soared from 33.26 million in March 2021 to 143.02 million by November 2024. While men continue to dominate in account numbers, female account holders also grew significantly—from 6.67 million in 2021 to 27.71 million in 2024.
Entrepreneurship:
An upward trend has been observed in female-headed proprietary establishments across manufacturing, trade, and service sectors between 2021 and 2024. Similarly, startups recognized by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) with at least one-woman director rose from 1,943 in 2017 to 17,405 in 2024.
Political Participation:
The total electorate has grown from 173.2 million in 1952 to 978 million in 2024. Women’s participation in elections continues to climb, with the female voter turnout recorded at 65.8% in 2024. While slightly lower than 67.2% in 2019, this still represents a narrowing gender gap, as female turnout surpassed that of males in 2024.
This publication is instrumental in identifying policy priorities and development strategies. By presenting a gender-focused lens on India’s socio-economic landscape, it supports the country’s commitment to achieving gender equity and sustainable development goals. The full report is available on the official MoSPI website at https://mospi.gov.in.






